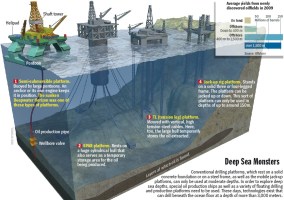
Caption: Bollen 1910 Monster der Tiefsee Offshore-Förderung Halbtaucher-Plattform SPAR-Plattform TL Tension Leg Plattform Hubbohrinsel Ölbohrinsel Deepwater Horizon Förderturm Ponton Ölfelder Barrel Ozeanboden 3D Erdöl Förderung Ölförderung Öl
Datum: 10. Mai 2010
Average yields from newly discovered oilfields in 2009
On land
Offshore
Down to 400 m
400 m to 1500 m
over 1,500 m
50 100 150
Millions of barrels
Source: Offshore
Helipad
Shaft tower
Pontoon
Oil production pipe
Wellbore valve
Layers at which oil is found.
1 Semi-submersible platform. Buoyed by large pontoons. An anchor or its own engine keeps it in position. The sunken Deepwater Horizon was one of these types of platforms.
2 SPAR platform. Rests on a huge cylindrical hull that also serves as a temporary storage area for the oil being produced.
3. TL (tension leg) platform. Moored with vertical, high tension steel cables. Here, too, the large hull temporarily stores the oil extracted.
4. Jack-up rig platform. Stands on a solid three or four-legged frame. The platform can be jacked up or down. This sort of platform can only be used in depths of up to around 150m.
Deep Sea Monsters
Conventional drilling platforms, which rest on a solid concrete foundation or on a steel frame, as well as the mobile jack-up platforms, can only be used at moderate depths. In order to explore deep sea depths, special oil production ships as well as a variety of floating drilling and production platforms need to be used. These days, technologies exist that can drill beneath the ocean floor at a depth of more than 3,000 meters.